Dr. Shahram Eivazi

University of Tübingen
Dpt. of Computer Science
Human-Computer Interaction
Sand 14
72076 Tübingen
Germany
- Telephone
- +49 - (0) 70 71 - 29 - 70494
- Telefax
- +49 - (0) 70 71 - 29 - 50 62
- shahram.eivazi@uni-tuebingen.de
- Office
- Sand 14, C220
- Office hours
- on appointment
Research Interests
- Eye tracking
- Machine vision
- Machine learning
- HCI and Human factors
- Medical technology
- Micro-neurosurgery
- Robotic
Current Projects
-
EyeMic, a binocular eye tracker that can be attached on top of any microscope ocular. (Video link)
This is the first step towards unrestricted eye tracking in microscopy procedures for development of future gaze-contingent microscope control systems.

Video -
A Head and Eye Tracking method for Hands-free Control of a Robotic system. (video link)
We are developing a head and gaze-contingent robotic exoscope for camera viewpoint automation.
Video -
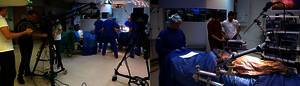
Gaze-Telesurgery for the SECTIO CHIRURGICA platform. Here we are developing a live gaze tracking system to be used for online training of surgeons.
Publications
2020
RemoteEye: An open-source high-speed remote eye tracker
Benedikt Hosp, Shahram Eivazi, Maximilian Maurer, Woflgang Fuhl, David Geisler, and Enkelejda Kasneci. Behavior Research Methods, pages 1–15. Springer, 2020.
Eye Tracking Data Collection Protocol for VR for Remotely Located Subjects using Blockchain and Smart Contracts
Efe Bozkir, Shahram Eivazi, Mete Akgün, and Enkelejda Kasneci. IEEE International Conference on Artifical Intelligence and Virtual Reality (AIVR), 2020.
2019
Improving Real-Time CNN-Based Pupil Detection Through Domain-Specific Data Augmentation
S. Eivazi, T. Santini, A. Keshavarzi, T. C. Kübler, and A. Mazzei. Proceedings of the 2019 ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications (ETRA) – To Appear, 2019.
2018
An Inconspicuous and Modular Head-Mounted Eye Tracker
S. Eivazi, T. Kübler, T. Santini, and E. Kasneci. Proceedings of the 2018 ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications (ETRA) , 2018.
BORE: Boosted-oriented edge optimization for robust, real time remote pupil center detection
W. Fuhl, S. Eivazi, B. Hosp, A. Eivazi, W. Rosenstiel, and E. Kasneci. Eye Tracking Research and Applications, ETRA, 2018.
2017
Using Eye Tracking to Evaluate and Develop Innovative Teaching Strategies for Fostering Image Reading Skills of Novices in Medical Training
N. Castner, S. Eivazi, K. Scheiter, and E. Kasneci. Eye Tracking Enhanced Learning (ETEL2017), 2017.
Towards Intelligent Surgical Microscopes: Surgeons Gaze and Instrument Tracking
Shahram Eivazi, Wolfgang Fuhl, and Enkelejda Kasneci. Proceedings of the 22st International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, IUI 2017. ACM, 2017.
Towards automatic skill evaluation in microsurgery
Shahram Eivazi, Michael Slupina, Wolfgang Fuhl, Hoorieh Afkari, Ahmad Hafez, and Enkelejda Kasneci. Proceedings of the 22st International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, IUI 2017. ACM, 2017.
Optimal eye movement strategies: a comparison of neurosurgeons gaze patterns when using a surgical microscope
S. Eivazi, A. Hafez, W. Fuhl, H. Afkari, E. Kasneci, M. Lehecka, and R. Bednarik. Acta Neurochirurgica, 2017.
2015
Automated Visual Scanpath Analysis Reveals the Expertise Level of Micro-neurosurgeons
T. C. Kübler, S. Eivazi, and E. Kasneci. MICCAI 15 Workshop on Interventional Microscopy, 2015.
Teaching
| Course | Term |
|---|---|
| Teamprojekt: Web Pages Personalization using Reinforcement Learning Technology |
